How To Find Bulk Density Of Sand
The density of Cement, Sand and Aggregate
Density, also known as the unit weight, is the mass per unit book of the textile. The symbol RHO (ρ) denotes it. It explains the caste of compactness of a textile. If the density of whatever substance is high, that means it is denser.
Mass per unit of measurement book of any construction material refers to its density. It is presented in Kg/k 3 or lb/ft 3 and shows the construction cloth'due south compactness.
Density can exist stated as ρ = m / v = one/v
Where
ρ = Density
chiliad = Mass
Five = Book
Density of Cement
A cement is a binding substance utilised in structure work that hardens and gains forcefulness speedily underwater.

Merely cement is unusually used; it is used to bind coarse and fine aggregate to produce mortar and physical. The cement is mixed with fine aggregate to have mortar for plaster and masonry, and with sand and coarse aggregate to give physical.
Equally I said, earlier density is the material's mass per unit volume. Since we measure mass in kg or lb and book in litre or cubic meter or cubic anxiety, hence density is stated in Kg/m 3 or lb/ft 3. The density of OPC cement is = 1440 Kg/1000 3.
Also Read – Difference Between OPC and PPC Cement
Sand Density
The density of sand varies according to its atmospheric condition ( Dry or Wet or packed).

The density of sand may modify if information technology is in a dry out or wet condition equally well every bit a loose and compacted country. When sand is packed, sand particles are forced to grade a narrow disposition, resulting in more than cloth in the book.
When sand is in wet status, water is present in sand particles that modify material quantity in the book. The average density of sand in a dissimilar state are as follows:
Loose Sand Density: 1442 Kg/m iii
Dry Sand Density: 1602 Kg/m iii
Packed Sand Density: 1682 Kg/thousand three
Packed Sand Density: 2082 Kg/m iii
Likewise, Read – Silt Content Exam for Sand
Density of Aggregate
Aggregates are chemically idle substances that are bonded by cement paste to make physical. Aggregates produce the majority of the total concrete's volume; hence, they affect concrete strength significantly.
Based on their size, the aggregates are named as:
- Fine Aggregate
- Fibroid Aggregate
The textile below 4.75 mm size refers to fine amass. The percentage of all types of harmful matter in fine aggregate should not surpass 5%. Crushed stone dust or natural sand is the fine aggregate chiefly utilised in the concrete mix.
Sand may exist collected from the river, ocean, lake or pit. Still, when used in the physical mix, it should exist adequately cleaned and tested to determine that the full percentage of silt, salts, clay and other such organic stuff does not pass the defined limit.

The substance that particles are retained on IS sieve no 480 (4.75mm) refers to coarse amass. The Nature of the work decides which size of coarse amass should be used.
The maximum size may be twenty cm for mass concrete, such as in dams etc. and 63 mm for plain cement concrete work.
For reinforced cement physical work unremarkably, 20 mm size aggregate is preferred. For structural concrete common materials like gravel and crushed stone are used.
Also, Read – What is M Sand? Properties, advantages, Disadvantages.
Bulk density of Aggregate
It is the weight of aggregate needed to make full a unit volume of the container. It helps to convert quantities by weight to past book. It also indicates the amass grading and shape.
Majority Density = Weight of aggregate / Container of unit volume
Unit: Kg/m iii or lb/ft iii
Essential Points
- Majority density is equal to mass if the volume is unit.
- In the above definition, the volume contains both aggregates forth with voids between aggregate particles.
- The approximate value of bulk density for aggregate commonly used for normal-weight concrete varies between 1200-1750 Kg/g 3 or 75 to 110 lb/ft 3 .
Relative Density or Specific Gravity of Aggregate
Aggregate Contains both permeable and impermeable pores. The specific gravity of aggregate excluding all pores is referred to as the absolute specific gravity. It is described as
Absolute Specific Gravity = (Weight of oven-dried aggregate at 100°c for 24 hours) / (Weight of water's volume equal to that of aggregate'southward solids excluding pores)

Essential Points
- Most of the aggregates possess a relative density within 2.4 – ii.ix with a similar particle density about 2400-2900 Kg/g 3 (150-181 lb/ft 3 ).
- Hereabouts, for coarse aggregates, the standard test process has been described in ASTM C 127(AASHTO), and for fine aggregates, the standard test practice has been described in ASTM C 128 (AASHTO).
- An aggregate relative density tin be decided based on over dry or saturated surface dry.
The absolute specific gravity is unremarkably not needed in concrete engineering. If only permeable pores are considered, and the textile'south solid volume is excluded, then the resulting specific gravity refers to credible specific gravity. It is represented every bit
Apparent specific gravity = (Weight of oven-dried Aggregate at 100°c for 24 hours) / (Weight of water's volume equal to that of aggregate'southward solids excluding permeable pores)

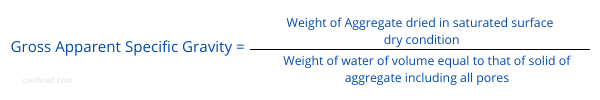
In concrete applied science, specific gravity based on a saturated surface dry condition is by and large used. It is referred to gross apparent specific gravity and is represented as
Gross apparent specific gravity = (Weight of dried amass in saturated surface dry status) / (weight of water'south volume equal to that of aggregate, including all pores)
Density of Edifice Materials As Per IS 875 Part-1
Conversion:
ane KN/m3 = 101.9716 kg/m3 say = 100 kg/grandiii (round off)
1 Kg/mthree = 0.0624 lb/ft3
| Structure Materials | Density in Kg/miii | Density in KN/m3 | Density in lb/ft3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitumen | 1040 | 10.iv | 64.896 |
| Brick Dust (Surkhi) | 1010 | 10.ane | 63.024 |
| Cement Mortar | 2080 | 20.viii | 129.792 |
| Chalk | 2100 | 21 | 131.04 |
| Dirt Soil | 1900 | xix | 118.56 |
| Earth (Dry) | 1410-1840 | 14.1-18.four | 87.98-114.82 |
| Earth (Moist) | 1600-2000 | xvi-20 | 99.84-124.eight |
| Fire Bricks | 2400 | 24 | 149.76 |
| Glass | 2500 | 25 | 156 |
| Granite Rock | 2400-2690 | 24-26.9 | 149.76-167.85 |
| Gypsum Mortar | 1200 | 12 | 74.88 |
| Gypsum Powder | 1410-1760 | 14.1-17.6 | 87.98-109.82 |
| Ice | 920 | 9.2 | 57.408 |
| Lime Mortar | 1600-1840 | 16-xviii | 99.84-114.82 |
| Ordinary Cement | 1440 | xiv.4 | 89.856 |
| PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) | 2400 | 24 | 149.76 |
| Pitch | 1010 | ten.1 | 63.024 |
| Prestressed Cement Concrete | 2400 | 24 | 149.76 |
| Rapid Hardening Cement | 1280 | 12.8 | 79.872 |
| RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) | 2500 | 25 | 156 |
| RCC Blocks | 2100 | 21 | 131.04 |
| Carmine Bricks | 1920 | 19.ii | 119.808 |
| Road Tar | 1010 | 10.one | 63.024 |
| Prophylactic | 1300 | 13 | 81.12 |
| Sal Wood | 865 | 8.65 | 53.976 |
| Saline Water | 1025 | 10.25 | 63.96 |
| Sand (Dry) | 1540-1600 | xv.4 -16 | 96.09 – 99.84 |
| Sand (Wet) | 1760-2000 | 17.6 – 20 | 109.82 -124.8 |
| Sissoo Wood | 785 | vii.85 | 48.984 |
| Steel (Mild) | 7850 | 78.five | 489.84 |
| Stone Ballast | 1720 | 17.2 | 107.328 |
| Stone chips | 1600 -1920 | xvi -nineteen.two | 99.84 -119.81 |
| Stainless Steel | 7480 | 74.8 | 466.752 |
| Teak Wood | 640 | 6.4 | 39.936 |
| Water | chiliad | x | 62.4 |
There are several materials used in edifice construction work. In the above tabular array, we have tried to comprehend the density/unit weight of mostly used building materials. I hope information technology helps yous.
Thank you!
Also, Read
Unit Weight of Building Materials Used in Construction
Divergence Betwixt Pre Tensioning and Post Tensioning
Water Cement Ratio – Definition, Importance, Calculation
What is curing of Concrete? – Purpose, Importance, Curing Period & Method
What is Plinth Beam? – Plinth Protection, Difference Between Plinth Beam and Tie Axle
Source: https://www.civillead.com/density-of-cement-sand-and-aggregate/
Posted by: hillruslaideemin.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Find Bulk Density Of Sand"
Post a Comment